
Transmission mode (Data Flow) In Data Communication
Transmission mode refers to the mechanism of transferring of data between two. devices connected over a network. It is also called Communication Mode. These. modes direct the direction of flow of information.
Communication between two devices can be simplex, half-duplex, full-diplex
Simplex:
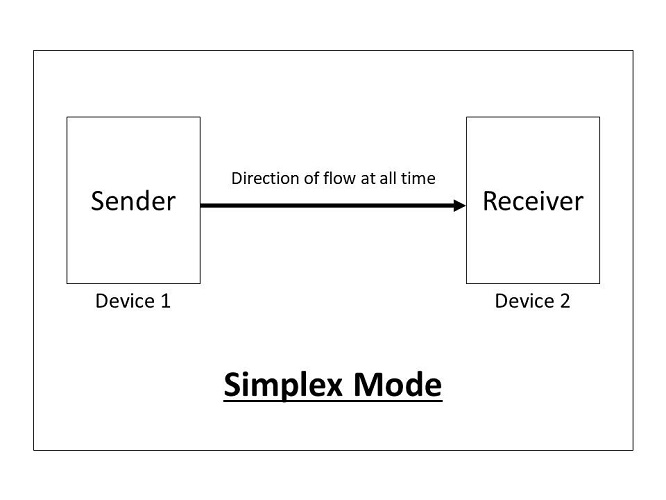
In simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, as on a one-way street. Only one of the two devices on a link can transmit; the other can only receive. Keyboards and traditional monitors are examples of simplex devices. The keyboard can only introduce input; the monitor can only accept output. The simplex mode can use the entire capacity of the channel to send data in one direction.
Half-duplex:
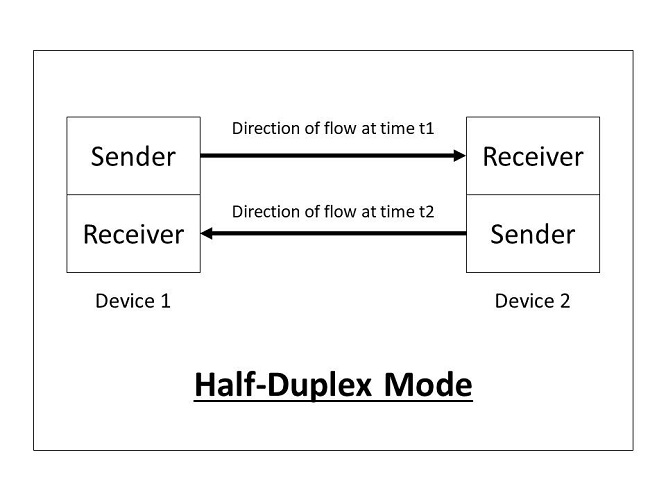
In half-duplex mode, each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice vers.
The half-duplex mode is used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time; the entire capacity of the channel can be utilized for each direction
Full- Duplex:
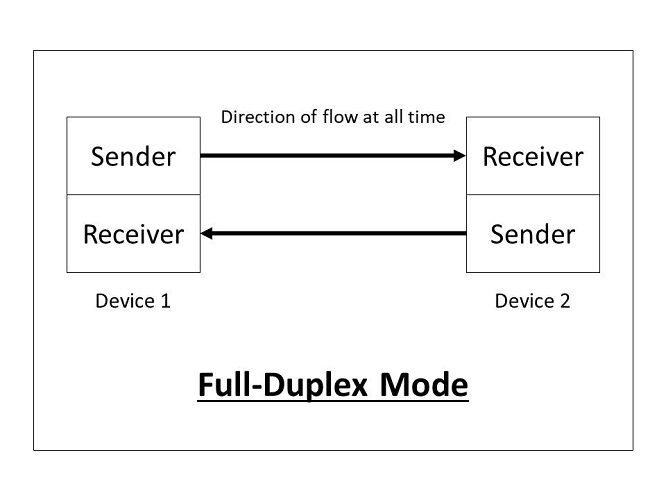
In full-duplex mode (also called duplex), both stations can transmit and receive simultaneously.
The full-duplex mode is used when communication in both directions is required all the time. The capacity of the channel, however, must be divided between the two directions.



Nice Article. Very useful Information. Thanks..
Abhay Kumar
1 year ago